
Improve Wind Turbine Reliability With Lubricant and Grease Analysis
Eurofins TestOil’s wind turbine oil analysis program can provide important information about the condition of your lubricants and equipment. Utilizing trend-based analysis will help minimize equipment downtime, enable more efficient maintenance activities, and protect warranty claims.
Oil analysis on wind turbines is an effective tool for monitoring:
- Lubricant Condition • Contamination • Mechanical Wear
View sample reports:
Where To Collect A Sample
There are several components of a wind turbine that are critical to operation and those that will incur substantial costs due to unplanned maintenance and downtime and should be considered for testing.
Critical components include: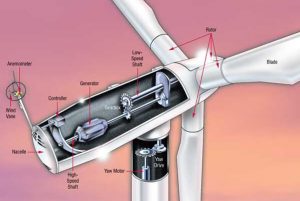

- Turbine Gearbox
- Main Shaft Bearing
- Generator Bearings
- Hydraulic Pitch System
- Pitch Drive Gears
- Pitch Bearings
- Yaw Drive Gears
- Yaw Bearings
Request More Information
Learn how you can significantly improve wind turbine reliability with Eurofins TestOil’s world-class oil and filter debris analysis.

Grease Analysis
Grease Analysis
Grease-lubricated bearings in wind turbines should be included in an effective condition monitoring program. At TestOil, we offer multi-faceted analysis to detect wear particles, contaminants and additives for in-service greases. Through routine sampling we are able to trend the data to identify potential problems before a major repair is required.
Wear metals are analyzed elementally via spectroscopic analysis to target the smaller, normal wear particles, and contrasted against Ferrous Wear Concentration which also detects larger, ferrous wear particles. Optionally, we may also perform Analytical Ferrography for determination of the wear mechanisms and severities of observable wear particles.
The additives are verified to ensure the correct grease is in use and not contaminated with another product. Contaminants, both particulate and water, are measured to determine when contaminants are increasing to a detrimental level.

